Open Ethics x Pirate Night Workshop: The Transparency Circle

In this article, we take a closer look at the Open Ethics x Pirate Night Workshop that revealed why traditional approaches to AI transparency fall short and what actually works.
When Alice Pavaloiu and the Open Ethics team set out to bridge the gap between AI ethics intentions and real-world implementation, they discovered something most workshops miss: people already know ethics matters. The challenge isn’t awareness but it’s the practical infrastructure to act on that knowledge.
On August 28, 2025, at Odonien in Cologne, this insight shaped an unconventional workshop approach that combined Open Ethics’ systematic transparency framework with Pirate Night’s raw, authentic startup culture. What emerged were conversations about AI ethics implementation that participants described as the most honest they’d experienced.
The Implementation Gap Problem
The gap between AI ethics awareness and practical implementation represents one of the most significant challenges facing the technology industry today, where despite widespread recognition of ethical principles, organizations struggle to translate good intentions into systematic practices. While awareness of AI ethics has reached near-universal levels among technology professionals, the translation of ethical intentions into systematic implementation remains frustratingly elusive.
The Open Ethics initiative, led by co-founder Alice Pavaloiu alongside contributors Ayşenur Kölgesiz and Tim Haeussler, designed an experimental workshop format to investigate why traditional approaches to AI transparency fall short and identify what actually drives behavior change.
The collaboration with Pirate Night, Cologne’s premier startup networking event, provided access to a diverse ecosystem of entrepreneurs, developers, and technology leaders who face daily decisions about AI implementation in resource-constrained environments.
Hands-On Ethics: The Physical Workshop Advantage
The breakthrough in workshop design came through creating 42 value stickers representing concrete ethical principles. Rather than abstract discussions, participants physically selected values that resonated with their personal ethics and applied the stickers to themselves as personal value badges. The stickers served as conversation starters that made abstract concepts tangible, with visible differences (such as one participant choosing ‘Trust’ while another selected ‘Efficient’) sparking authentic discussions about trade-offs in AI development.
This design choice eliminated typical workshop dynamics where participants give socially acceptable answers. When people physically handled and arranged concrete values, they admitted implementation failures they wouldn’t discuss in purely verbal formats. The physical interaction bypassed professional facades that typically prevent honest ethics conversations.
The stickers were designed as conversation starters that made abstract concepts tangible. When someone chose ‘Trust’ and their neighbor chose ‘Efficient,’ that difference sparked authentic discussions about trade-offs in AI development.
The Odonien Effect
The venue choice proved crucial to the workshop’s success. Odonien, Cologne’s largest sociocultural venue, merges an open-air studio, nightclub, cultural center, and workshop facility into one inspiring industrial-artistic environment. Towering sculptural installations made from reclaimed materials created an authentic atmosphere that gave participants permission to discuss real challenges without maintaining corporate-polished personas.
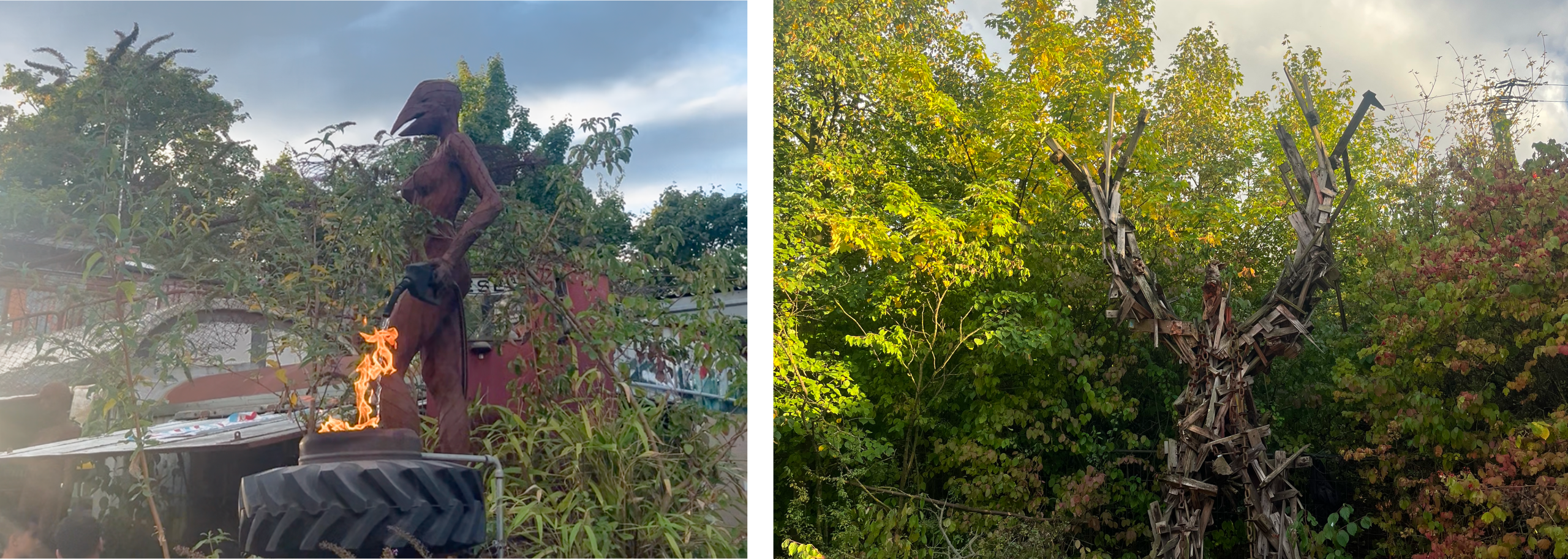

photos taken by @aysenurkolgesiz – www.aysenurkolgesiz.com
Systematic Design Behind Spontaneous Conversations
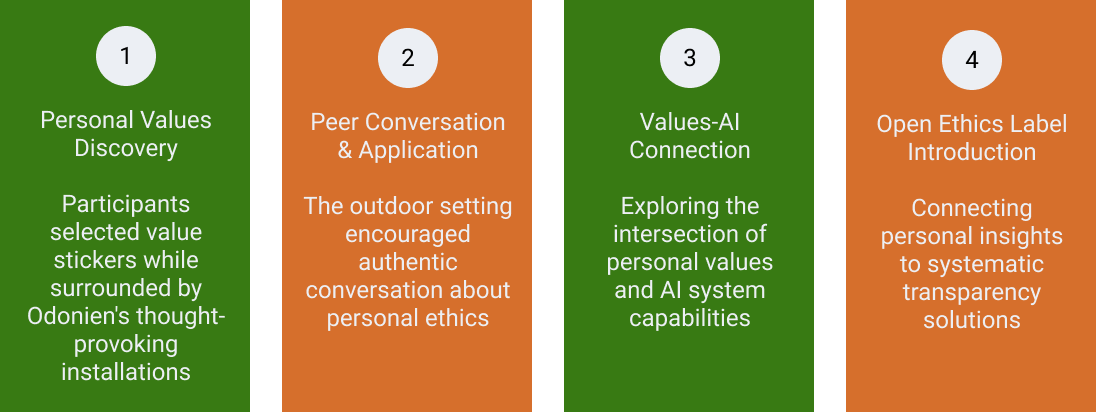
While the conversations felt organic, the Open Ethics workshop team guided participants through a carefully structured progression designed to build authentic engagement. The four-phase journey moved from individual values discovery through peer dialogue to AI integration and systematic transparency introduction.
This sequencing proved critical: participants who engaged with early personal questions were three times more likely to commit to concrete implementation steps.
Following a comprehensive ideation session and thorough exploration of the Open Ethics Initiative’s core principles and the Open Ethics Label framework, the following steps have been followed:
Perhaps the most significant insight challenged conventional assumptions about ethics adoption. While regulatory pressure often dominates AI ethics discussions, 70% of workshop participants expressed strong interest in peer accountability partnerships voluntary community mechanisms for ongoing transparency support.
Following completion of the structured workshop progression, participants were invited to participate in a comprehensive follow-up survey designed to capture quantitative insights alongside the qualitative observations from the workshop sessions. This mixed-methods approach enabled the research team to validate workshop observations with measurable data and identify patterns that might not have emerged through facilitated discussions alone. The survey, distributed via QR-code integration developed during the analog-digital workshop design process, achieved a response rate that provided meaningful insights into participant perspectives on AI ethics implementation, personal values alignment, and transparency adoption barriers. The combination of immediate workshop engagement followed by reflective survey responses informed both the key findings presented in this article.
This dual approach proved essential for distinguishing between performative responses during group discussions and genuinely held perspectives that participants were more willing to express in anonymous survey formats, a distinction that became crucial for understanding the true scope of the implementation gap between ethical intentions and organizational practices.
Survey Validation of Workshop Insights
Post-workshop survey data provided quantitative validation of the qualitative observations, revealing critical patterns in AI ethics adoption and transparency expectations:
Graduated Transparency Needs: While explainability requirements showed moderate adoption (50% requiring explanations for important decisions), concerns about value alignment (75%) and security (75%) revealed the nuanced landscape of user expectations beyond basic functionality.
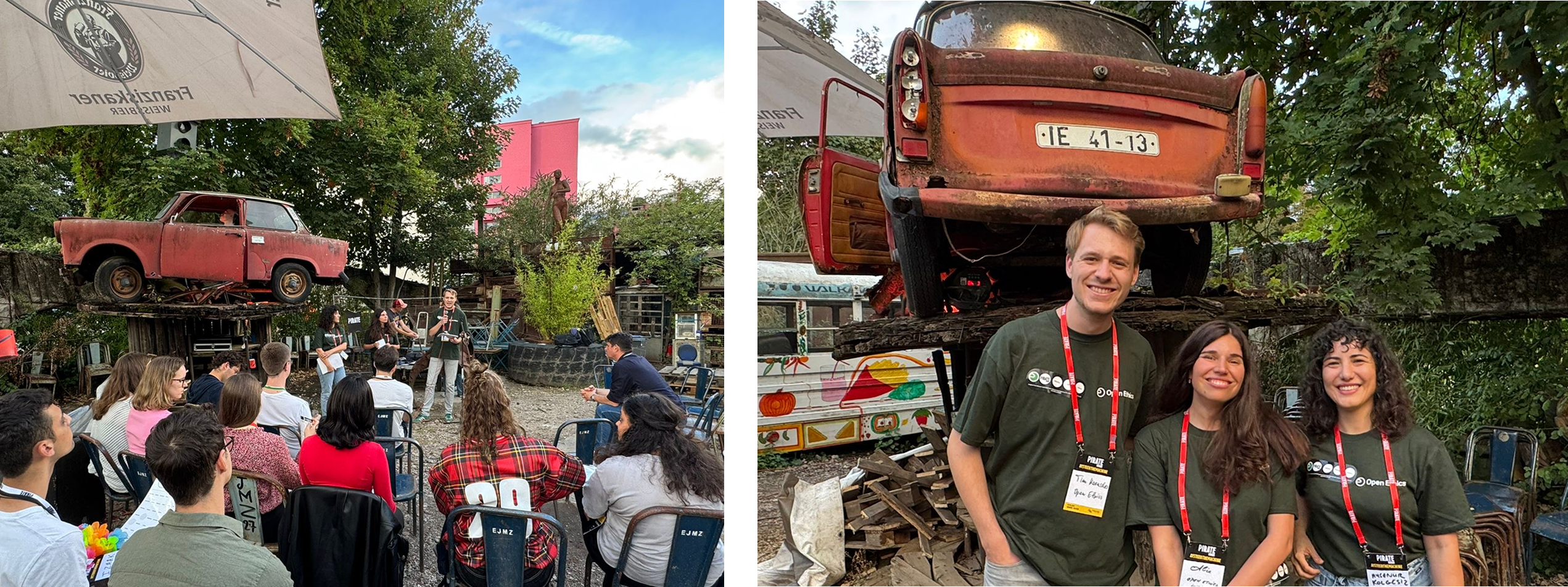

Conducted workshop with Tim Haeussler, Alice Pavaloiu and Ayşenur Kölgesiz
The Path Forward
The workshop demonstrated that the gap between AI ethics intentions and implementation isn’t inevitable but is a design challenge that can be addressed through thoughtful community building, practical tools, and authentic conversation spaces.
The workshop insights revealed the urgent need for systematic transparency infrastructure which is precisely what the Open Ethics Label addresses by providing a standardized framework that makes ethical commitments visible and actionable for both developers and users.
To understand why labeling represents a crucial infrastructure component, Open Ethics Initiative draws from the food industry analogy. The reason consumers can make informed choices about food is because we have established a common language for discussing nutrition facts. We all consume food and have learned to understand what’s inside the package: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and even recycling information printed directly on packaging. Yet when it comes to data and decision technologies, do we truly know what’s inside? Today’s primary tool for digital transparency, privacy policy pages, falls short of this standard. These documents are lengthy, complex, and rarely read by users, creating an information asymmetry that undermines informed consent and user agency.
The Open Ethics Label
The Open Ethics Label (OEL) represents the first level of the Open Ethics Maturity Model (OEMM), designed to provide accessible information about digital solutions to enhance transparency and build user trust. Unlike conventional labeling systems, the OEL signifies a product owner’s commitment to transparency through direct, verifiable reflection of public self-disclosure processes.
The label encompasses critical details including approaches to algorithmic and data transparency, safety precautions for system output modulation, and clear documentation of ethical frameworks guiding development decisions. This systematic approach transforms abstract ethical commitments into concrete, actionable transparency measures that users can understand and evaluate.
Aligned with the EU Commission’s white paper framing an “Ecosystem of Trust”, the Open Ethics Label addresses Requirement 5.G for “voluntary labeling for no-high risk AI applications.” The framework enables economic operators not covered by mandatory requirements to voluntarily adopt transparency standards and receive quality labels for their AI applications, creating market incentives for ethical development practices.
The Open Ethics Label features a clean, standardized format with the distinctive green Open Ethics logo, designed as a “nutrition label” for digital products that provides systematic transparency documentation for AI systems.
Conclusion
The Open Ethics Label, developed through insights like these, provides a standardized framework for AI transparency that integrates with existing development workflows. By making abstract values tangible and providing practical implementation tools, Open Ethics is building the infrastructure necessary for scaling authentic AI transparency across the technology ecosystem.
The label encompasses critical details including approaches to algorithmic and data transparency, safety precautions for system output modulation, and clear documentation of ethical frameworks guiding development decisions. This systematic approach transforms abstract ethical commitments into concrete, actionable transparency measures that users can understand and evaluate.
For organizations ready to bridge the implementation gap between ethical intentions and systematic practice, the Open Ethics Label offers a proven pathway from awareness to action and creating the common language for digital ethics that the industry urgently needs.
See the full case study behind preparing the workshop
Learn more about creating transparency documentation for your AI systems:
Visit the Website of Open Ethics Initiative
Generate your Open Ethics Label
Featured image credit: ©aysenurkolgesiz
