Open Ethics Maturity Model
OEMM v1.0.0
The Open Ethics Maturity Model (OEMM) is a five-level framework. It embarks the organization on a journey toward transparent governance of AI and autonomous systems.
What is it?
The framework offers a systemic approach on a set of levels: from awareness – to governance. Each level has a focus on the organization becoming more open and transparent, improving its ethical posture, and covering elements such as team, accountability, risk assessment, robustness, privacy, and policy compliance.
Who is it for?
Open Ethics Maturity Model was created for any organization:
- who aims to instill, strengthen and keep refining responsible practices for their autonomous systems throughout all stages of development and implementation.
- who wants to build transparent & trustworthy technology which adheres to ethical & value-based considerations.
- who would like to be equipped and mature to tackle ethical issues, while being consistent with the guidelines and regulatory standards in the area.
The unique feature of OEMM stems from the “open” aspect of the framework, underpinned initially by fostering an internal culture of transparency within the organization. It is gradually extending this ethos outwards, by making it transparent to its stakeholders and a wider public.
How is OEMM designed?
Having governance as the north star of the journey allows the organization to steer toward alignment by taking concrete actions, enhance transparency overall and have increased adaptability and ease of adopting solutions in the complex and dynamic landscape of AI.
The Open Ethics Maturity Model is designed to be agnostic, allowing for the use of any external tools and technology. At the same time, the Open Ethics Initiative provides open tools and technology for navigating the levels of the model.
Great things are not done by impulse, but by a series of small things brought together.Vincent Van Gogh
Levels of the Open Ethics Maturity Model
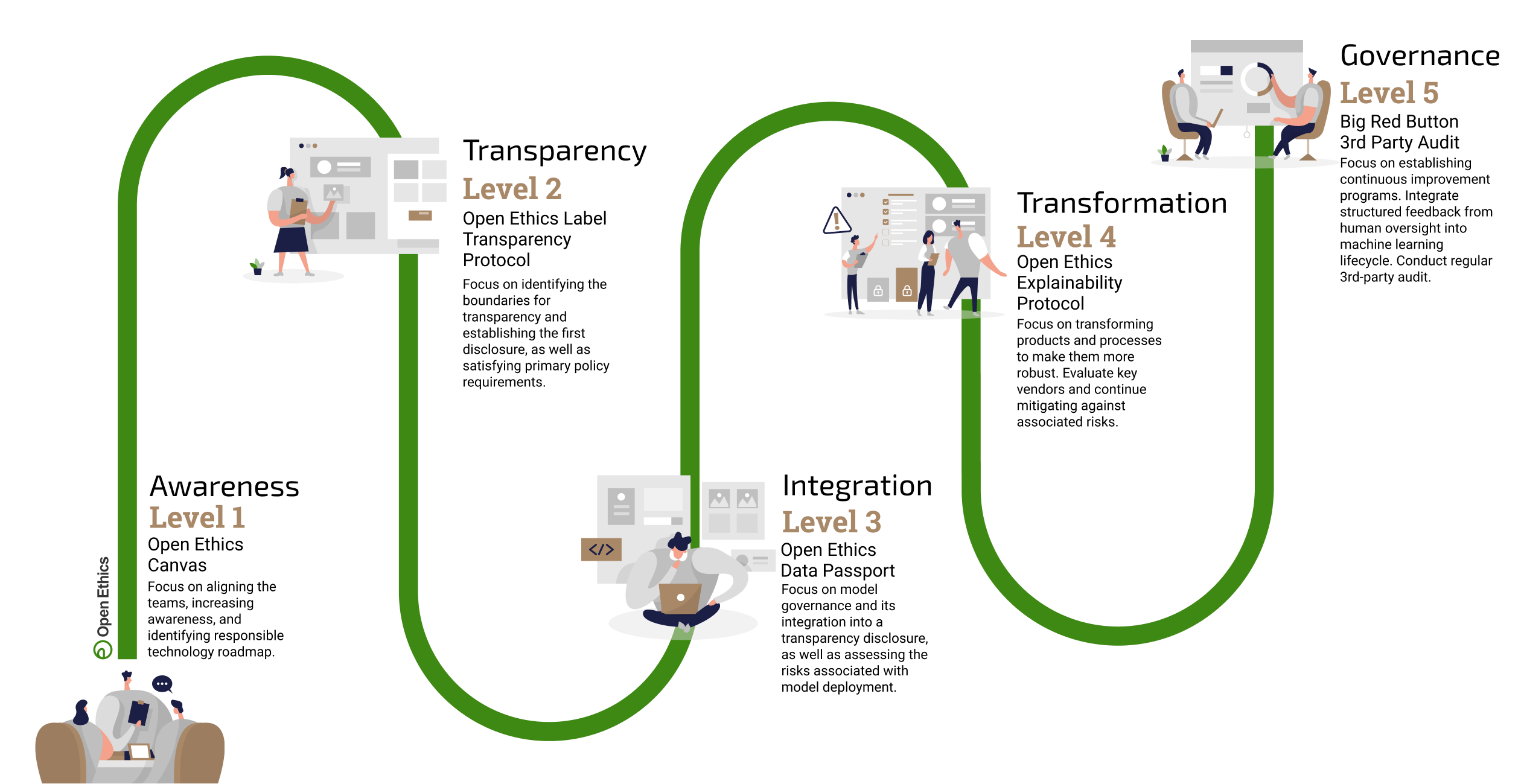
Level 1: Awareness
Tools: Open Ethics Canvas
The primary focus of this level is placed on setting up & aligning the teams, increasing awareness within the organization, and giving a start to the responsible technology roadmap. The Open Ethics Canvas can be used to enable a multidisciplinary dialogue and can weigh in on strategy and policy.
Level 2: Transparency
Tools: Open Ethics Label & Open Ethics Transparency Protocol
This level engages the team to identify the boundaries for transparency through internal dialogue and establish the first disclosure, as well as to satisfy the primary policy requirements. The Open Ethics Label (OEL) can be used by the organization to publish the first disclosure by describing the training data, algorithms and the decision space. The Open Ethics Transparency Protocol (OETP) is a documented way on how to generate, host, share, validate, and verify machine-readable disclosure in a standardized and explicit way, without compromising the IP or security. The organization should have the disclosure publicly available in the form of a machine-readable file and optionally, using a set of standard OEL icons.
Level 3: Integration
Tools: Data Passport
At the forefront of this level stands the integration of the training metadata (data about the training datasets and models) into a transparency disclosure, as well as assessing the risks associated with AI model deployment. A more in-depth disclosure of the models and datasets can be established and published by using the Data Passport, which should also be integrated into the disclosure. Both tools can be used iteratively to ensure continual improvement and safeguarding.
Level 4: Transformation
Tools: eXplainability Protocol
The focus of this level lies in transforming the products and processes to make them more robust. The organization evaluates key vendors and continues mitigating against associated risks. Safety measures are put in place and the AI is assessed by using the fairness and bias metrics scoped in the roadmap. The eXplainability Protocol (OEXP) can be used to enhance the explainability of the system outputs.
Level 5: Governance
Tools: Big Red Button and the 3rd Party Audit
This level focuses on establishing continuous improvement programs, integrating the structured feedback from human oversight into the machine learning lifecycle and conducting regular 3rd-party audits. Governance requires continuous improvement, crucial for the agility of the organization in a dynamic business and regulatory environment. Facilitating the access of a 3rd Party Audit leads to verification of the content accuracy of the disclosure, while the Big Red Button can be used to have algorithmic misuse, abuse, or discrimination reported.
Tools and Impact
| Culture | Transparency | eXplainability | Redress | Accountability | Control | Fairness | Privacy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Ethics Canvas | ||||||||
| OEXP – Explainability Protocol | ||||||||
| OETP – Transparency Protocol | ||||||||
| BRB – Incident Reporting | ||||||||
| Open Ethics Label | ||||||||
| Open Ethics Data Passport |
Actions and Outcomes
To provide a comprehensive overview of the OEMM framework and its approach, we curated the table delineating actions, and corresponding outcomes at each stage. This table serves as a roadmap, guiding organizations through the journey from awareness to governance. Stakeholders can gain insights and plan the sequential progression of their initiatives and the anticipated outcomes, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic alignment with the overarching goals of the OEMM framework.
Stages & Levels | Outcomes | Actions | Tools |
Level 1Awareness |
|
| Open Ethics Canvas |
Level 2Transparency |
|
| Open Ethics Label Open Ethics Transparency Protocol |
Level 3Integration |
|
| Data Passport |
Level 4Transformation |
|
| eXplainability Protocol |
Level 5Governance |
|
| Big Red Button 3rd Party Audit |
A new project?
If you want Open Ethics to help your organization in the journey toward transparency and safety with the OEMM framework, send us an email.
